Fix Virtual PC 2007 Shared Networking (NAT) Internet Not Working in Windows Server 2003, 2008 and Vista Guest OS
After installing Windows Server 2003, Windows Server 2008 and Windows Vista into Microsoft Virtual PC’s virtual machine (VM) (update to Virtual PC 2007 SP1) as guest operating system, and set the Networking Settings for the VM to use Shared Network (NAT) as the network adapter, the Internet appears to be not working where web browser (Internet Explorer, IE and Firefox) cannot connect, find, locate or browse to website.
However, when IP address is used, access to the external server on Internet may work. For example, ping, trace route, ftp, sftp, telnet and SSH using IP address instead of domain name or host name, user can successfully connecting to the remote server.
NAT (Network Address Translation) is an easy shared networking technique that masquerading or transceiving network traffic through a router that involves re-writing the source and/or destination IP addresses and the TCP/UDP port numbers of IP packets as they pass through. In the case of Virtual PC, it uses a virtual NAT router which built on host computer’s default active network connection to allow guest operating system to access Internet via the host’s Internet connection.
Shared Networking or NAT allows computers or hosts on a private network to access the Internet using a single IP address, without exposing the PCs (or virtual machines) to the external network, significantly reduce security risk. NAT is also useful to allow virtually unlimited number of IP addresses to connect to Internet, thus administrator is not limited by the amount of IANA assigned-IP address allocated space. Beside, Shared Network (NAT) allows user to easily plug and play or move the virtual machine or physical machine to different network configurations such as different Wi-Fi wireless access point, home or office network.
Most computers, including Virtual PC 2007 virtual machines can easily access Internet using Shared Networking, as easy as right after operating system is installed, which enable DHCP by default. So, the problem with Windows Server 2003, Server 2008 and Vista as guest OS cannot access Internet is by design. The Internet not working issue is caused by when the guest operating system queries for DNS Server from Shared Network (NAT) virtual router, the guest OS is configured to use the same DNS servers which are used by the physical host computer.
This is not the case with a Windows Server 2003 guest though. The problem is that Shared Networking configures the guest operating system to use the same DNS servers as are used by the physical computer. However, when actual DNS query resolving packets are been returned, it’s actually returned from the IP address of “192.168.131.254”, which is the virtual gateway used by Shared Networking (NAT).
Windows Server 2003, Windows Server 2008 and Windows Vista will reject any DNS resolution packets that are returned from a different source from than the DNS Server (both has different IP address) that it had requested the information from. As thus, all name resolution of domain name and URL fails, indirectly leads to the guest operating system appears to be cannot connect to Internet. Windows XP and older operating system is not affected by this behavior.
To fix the Shared Network (NAT) Internet no connection or not working issue, the resolution is to manually assign the IP address for the DNS Server for the guest operating system to 192.168.131.254, the virtual gateway IP address used by Virtual PC. To make the change (in guest operating system), open Network Connections folder (in Windows Vista, access via Network and Sharing Center), and right click Local Area Connection network icon to select its Properties. Then double click on Internet Protocl (TCP/IP) under General tab or Internet Protocol Version 4 (TCP/IPv4) under Networking (for Windows Vista) tab.
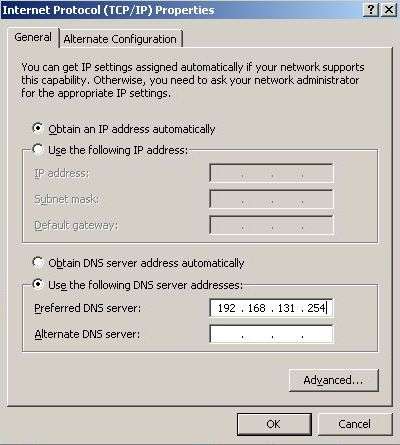
Click to select the radio button of Use the following DNS server addresses, and then type in 192.168.131.254 into the IP address box for Preferred DNS Server. Click OK twice to exit, and voila, the Shared Network (NAT) now works as it should with Internet access.
If you’re encountering this problem in Windows XP guest OS, it’s probably caused by invalid DNS server assigned by Virtual PC network adapter too.
Recent Articles
- How To Download HBO Shows On iPhone, iPad Through Apple TV App
- Windows 10 Insider Preview Build 19025 (20H1) for PC Official Available for Insiders in Fast Ring – Here’s What’s News, Fixes, and Enhancement Changelog
- Kaspersky Total Security 2020 Free Download With License Serial Key
- Steganos Privacy Suite 19 Free Download With Genuine License Key
- Zemana AntiMalware Premium Free Download For Limited Time